How to Use a Jigsaw Tool – A Comprehensive Guide
A jigsaw tool can be a game-changer for DIY enthusiasts and professional craftsmen alike. This versatile handheld saw has the ability to make intricate cuts in various materials, from wood to metal, and from straight lines to curves. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the features and components of a jigsaw, different cutting techniques, advanced applications, and tips for accurate and safe use. Let this be your roadmap to mastering the art of cutting with a jigsaw!
Short Summary
- Understanding the jigsaw and its components is important for achieving optimal cutting accuracy.
- Different types of blades are suited to different materials, while advanced applications enable users to create beveled cuts, cut sheet metal and ceramic tile.
- Adhering to safety guidelines such as wearing protective gear and using a straight edge guide will help maximize accuracy when operating a jigsaw safely.
Understanding the Jigsaw Tool
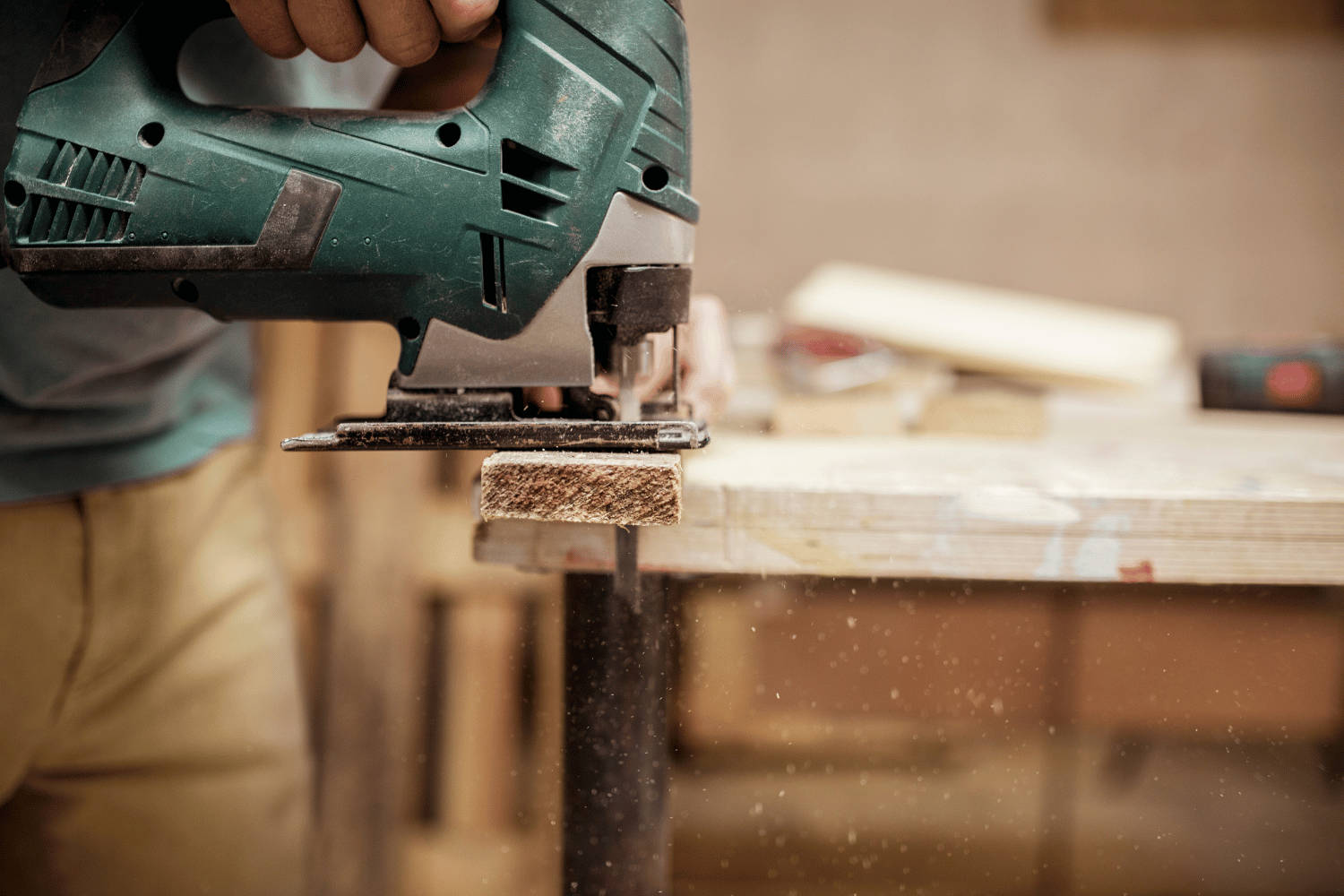

A jigsaw is a handheld saw that uses a thin, straight blade moving in an up-and-down motion. Jigsaws are powered by electricity and come as either corded or cordless models. This tool is designed to cut through various materials including wood, metal, laminate, and PVC, and is capable of making both straight and curved cuts with ease.
To achieve excellent results, it is essential to select the right blade for the material being cut. Different blades are designed for different materials, so it is important to choose the right one for the job. For example, a blade designed for cutting metal will not work as well on wood, and vice versa. Additionally, the type of blade used will also affect the quality of the cut.
Types of Jigsaw Blade
When it comes to jigsaw blades, there are four main types available: carbon steel blades, coarse-toothed blades, fine-toothed blades, and bi-metal blades. Hardened carbon steel blades are typically used for cutting through wood, PVC, or laminate.
Coarse-toothed blades, with fewer teeth per inch (2.5 cm), are ideal for quickly making cuts in wood, especially when equipped with a sharp blade tip. For good wood cutting blades, go with fine-toothed blades, which are the standard for creating a neat edge on wood, as they have more teeth per inch (2.5 cm).
For metal cutting blades, bi-metal blades are the perfect choice. They feature hardened steel teeth for efficient cutting and a soft, flexible body to prevent breakage. To ensure optimal results, it is important to find a blade or set of blades specifically designed for metal cutting.
Advantages of Using a Jigsaw
One of the main advantages of using a jigsaw is its ability to make a variety of cuts, including straight cuts, patterns, curves, and plunge cuts, in a wide range of materials. Its oscillating feature, which is a forward and backward rocking motion in addition to the up and down motion of the blade, allows for fast cutting, although it is not recommended for precise cutting or delicate materials.
Jigsaws are particularly well-suited for cutting curves and intricate shapes in wood. For example, constructing a wooden Christmas tree or a rocket bookshelf would be an ideal project for this power tool. However, they are not suitable for producing swift, extended, and precise cuts.
Essential Components of a Jigsaw
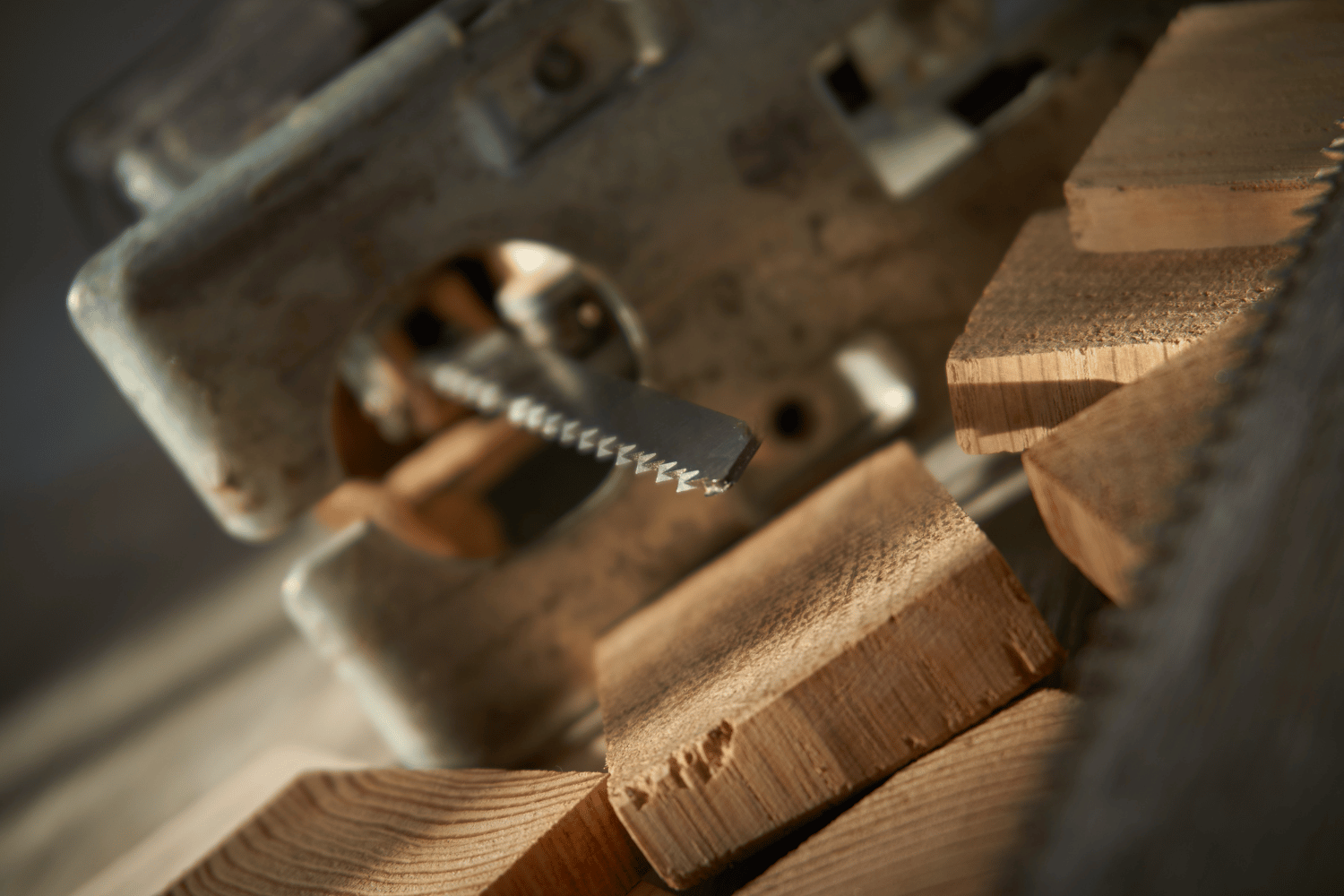
In order to make the most of your tool, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with its essential components. Jigsaws are equipped with two handle styles: the bow handle (D-handle) and barrel grip. The trigger operation is used to activate and deactivate the saw, while the trigger lock button ensures that the trigger remains securely locked in the “ON” position. An adjustable speed dial allows for modifying the blade speed to achieve optimal outcomes on a range of materials.
The orbital action switch is another notable feature, enabling the blade to oscillate in both the forward and backward direction, in addition to its usual up and down movement. This is advantageous for speedy cutting, but should be used with caution on delicate materials.
Lastly, the footplate or shoe, which is the base of the saw, rests against the material being cut and plays a vital role in ensuring cutting accuracy.
Saw Blade Types
When it comes to jigsaw blades, there are two main types to consider: the 1/4” wide blades and the 3/8” wide blades. The 1/4” wide blades are suitable for precise cutting around corners, while the 3/8” wide blades are suitable for general purpose cutting.
The most common blades are made of carbon steel, measuring 2 to 3-1/2 inches in length and either 1/4 or 3/8 inches in width. Six-teeth-per-inch blades are ideal for rapid, coarse cuts. Conversely, finer blades that have 10 or more teeth per inch cut with greater precision and finesse.
Additionally, toothless blades are available for cutting materials such as leather and tile.
Blade Clamp and Changing System
The blade clamp in a jigsaw serves to secure the blade in position. Replacing a jigsaw blade involves disengaging the blade from the clamp using the appropriate button or lever, then inserting the new blade with the teeth facing towards the front. T-shank blades are the most convenient for tool-free installation, as they can be easily pushed into the quick release until they snap into place.
When changing the blade, it is essential to consult your saw’s user manual for the appropriate instructions. If you no longer have the manual, you can likely locate a PDF version online by searching for your model number.
Base Plate or Shoe
The base plate, or shoe, of a jigsaw is a metal base that rests on the material being cut, commonly made out of aluminum, steel, or magnesium. It is essential for ensuring the cutting accuracy of the tool. Most shoes include adjustable features. This allows you to tilt the angle for beveled cuts.
On newer saw models, there is typically a convenient lever for adjusting the angle of the shoe. If no quick-release lever is present, a screw or small bolt can be loosened with the appropriate tool.
Cutting Techniques with a Jigsaw
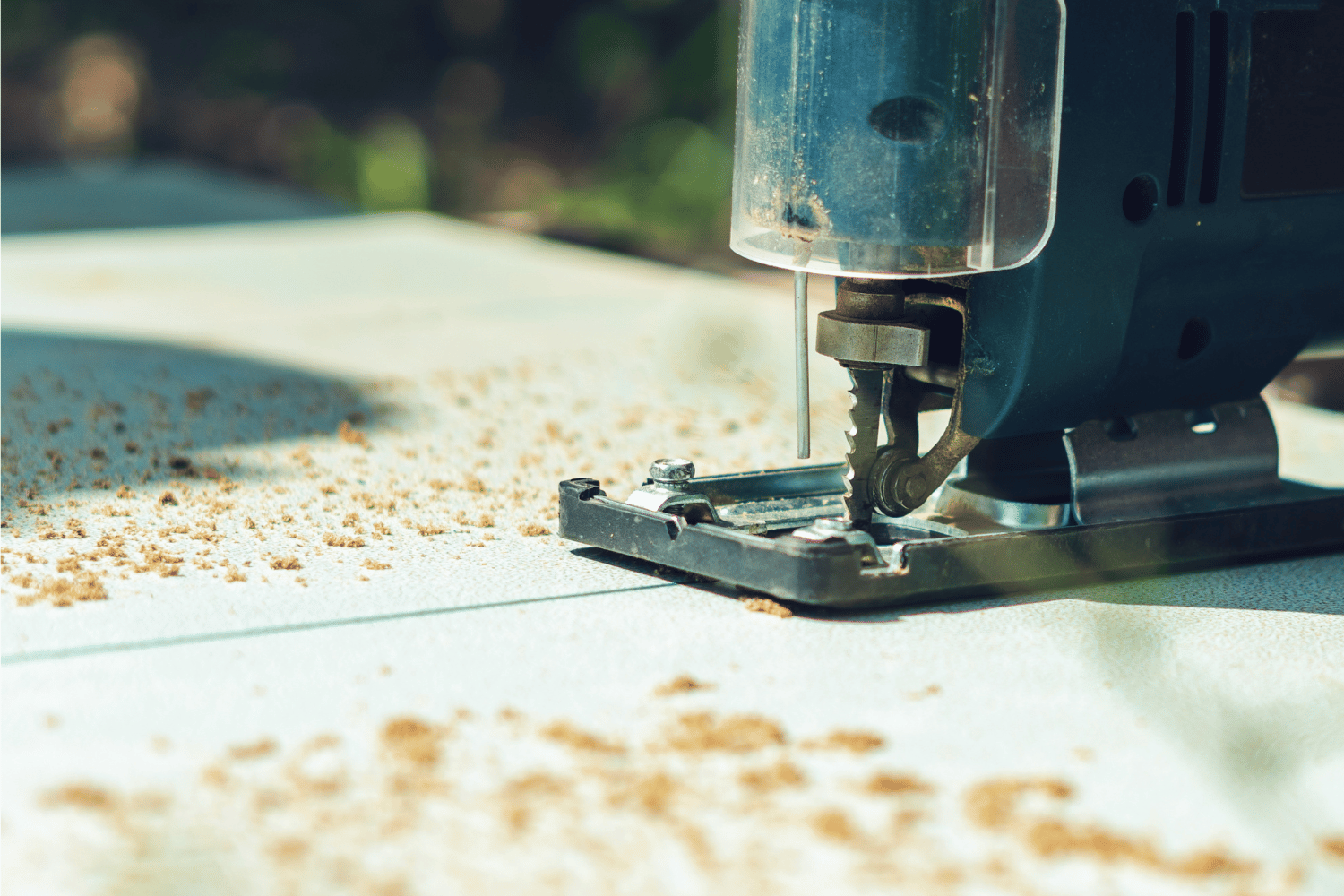

Mastering the art of cutting with a jigsaw involves learning different techniques for various applications. Common cutting techniques include cutting curves, straight lines, and holes. To avoid tear out on the top side of the piece when cutting, use a reverse-tooth blade. This type of blade cuts on the downstroke, minimizing the chance of splinters on the top surface of the material.
When cutting laminate with a jigsaw, it is essential to use a starter hole and ensure that the jigsaw blade extends at least one inch below the wood when fully extended. This will help to prevent chipping during the cutting process.
Cutting Curved Lines
To cut curved lines with a jigsaw, it is essential to use short relief cuts within the curves to facilitate the blade’s passage through the turn. To start, firmly press the saw shoe onto the workpiece with the blade facing away from the edge. This will help you maintain control during the cut and reduce the risk of the blade binding on tight curves.
Relief cuts are particularly useful for removing waste and preventing tear out when cutting tight curves with a jigsaw.
Cutting Straight Lines
To cut straight lines with a jigsaw, it is important to use a guide or straight edge to follow the cutting line. A jigsaw guide can be especially helpful for beginners who are still getting used to the tool. Remember, achieving a straight line while using a jigsaw requires practice and patience.
While a jigsaw is not the recommended tool for making fast, long, straight cuts in wood (a circular saw is a better option), it can still be used for short, precise cuts when a guide is used.
Cutting Holes and Openings
To cut a hole in the center of a material using a jigsaw, it is essential to first drill a starter hole close to the cut line within the desired hole. Using a down-cutting blade is recommended for cutting laminate with a jigsaw. Once the blade is inserted, proceed by cutting along the line.
When the cut is finished, remove the cut piece.
Advanced Jigsaw Applications
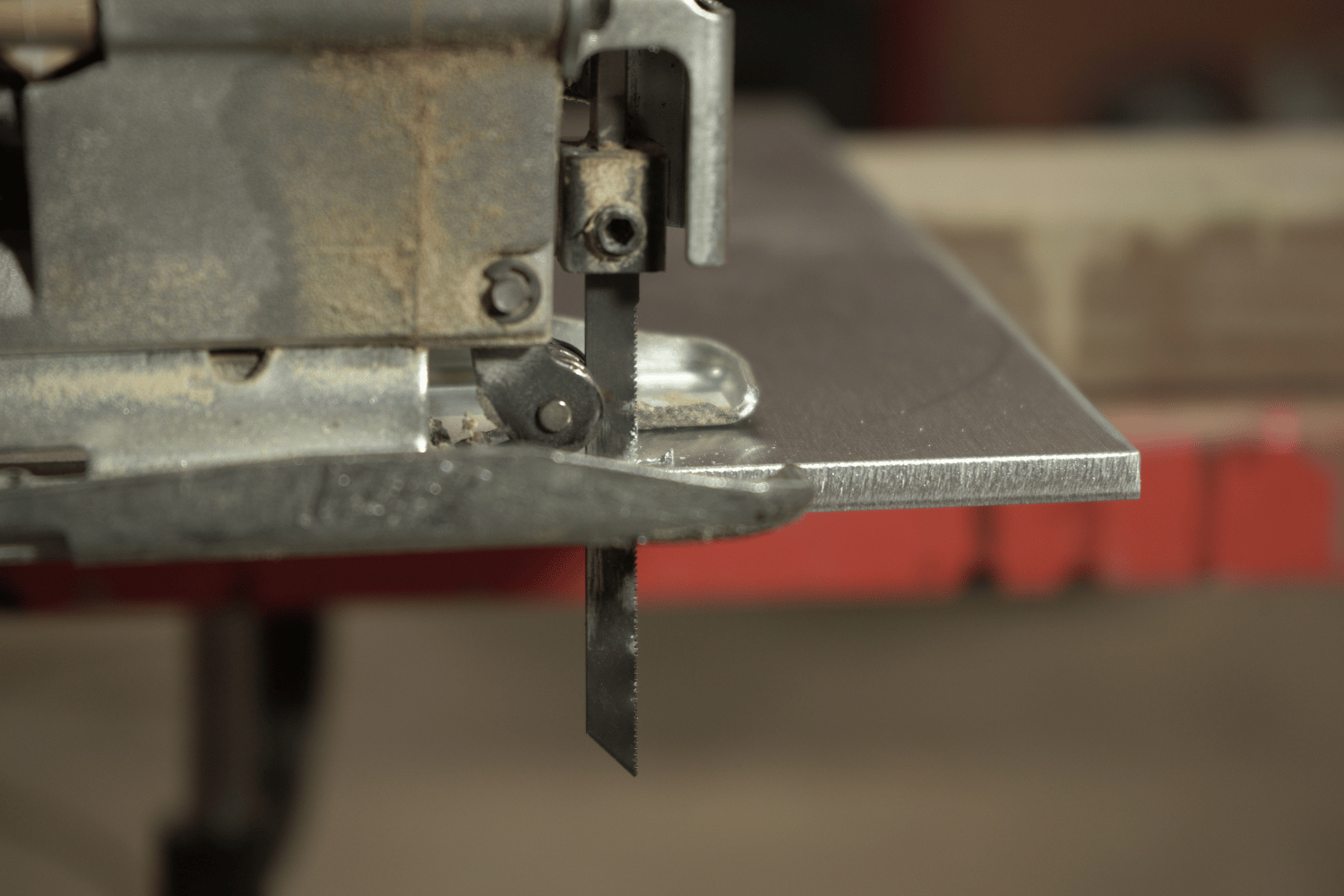
Beyond basic cutting techniques, a jigsaw can also be used for more advanced applications, such as creating beveled cuts, cutting sheet metal, and cutting tile and ceramic. By mastering these advanced techniques, you can further expand your skillset and take full advantage of the tool’s versatility.
Beveled Cuts
Creating beveled cuts with a jigsaw involves adjusting the angle of the blade and guiding it along the outside of the cutting line. It is essential to allow the blade to reach its full speed before introducing it into the workpiece, as this will help ensure precise cuts.
Cutting Sheet Metal
Cutting sheet metal with a jigsaw requires the use of a metal-cutting blade and some extra precautions to ensure safety and accuracy. One approach is the sandwich method, which involves layering the sheet metal between 1/4”-thick pieces of plywood and sawing carefully through all three layers using a jigsaw with an appropriate blade. This technique can help minimize the risk of injury and ensure a cleaner cut.
When cutting sheet metal, it is important to wear safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask. Additionally, ensure that the blade is sharp and properly installed, and secure the material to a stable surface to prevent shifting during the cut.
Cutting Tile and Ceramic
Cutting tile and ceramic with a jigsaw is possible when using a special toothless, carbide-grit blade. To avoid surface scratches, apply masking tape to either the face of the tile or the bottom of the jigsaw shoe, and draw the cutting guides on top of the tape. Ensure tile is clamped securely prior to cutting. This will prevent any shifting during the cut. Use a corresponding tile blade for best results.
When cutting tile and ceramic, the cutting should be done slowly and the blade should be allowed to do the work. This will help to ensure a clean, precise cut and minimize the risk of chipping or breaking the material.
Tips for Accurate and Safe Jigsaw Use
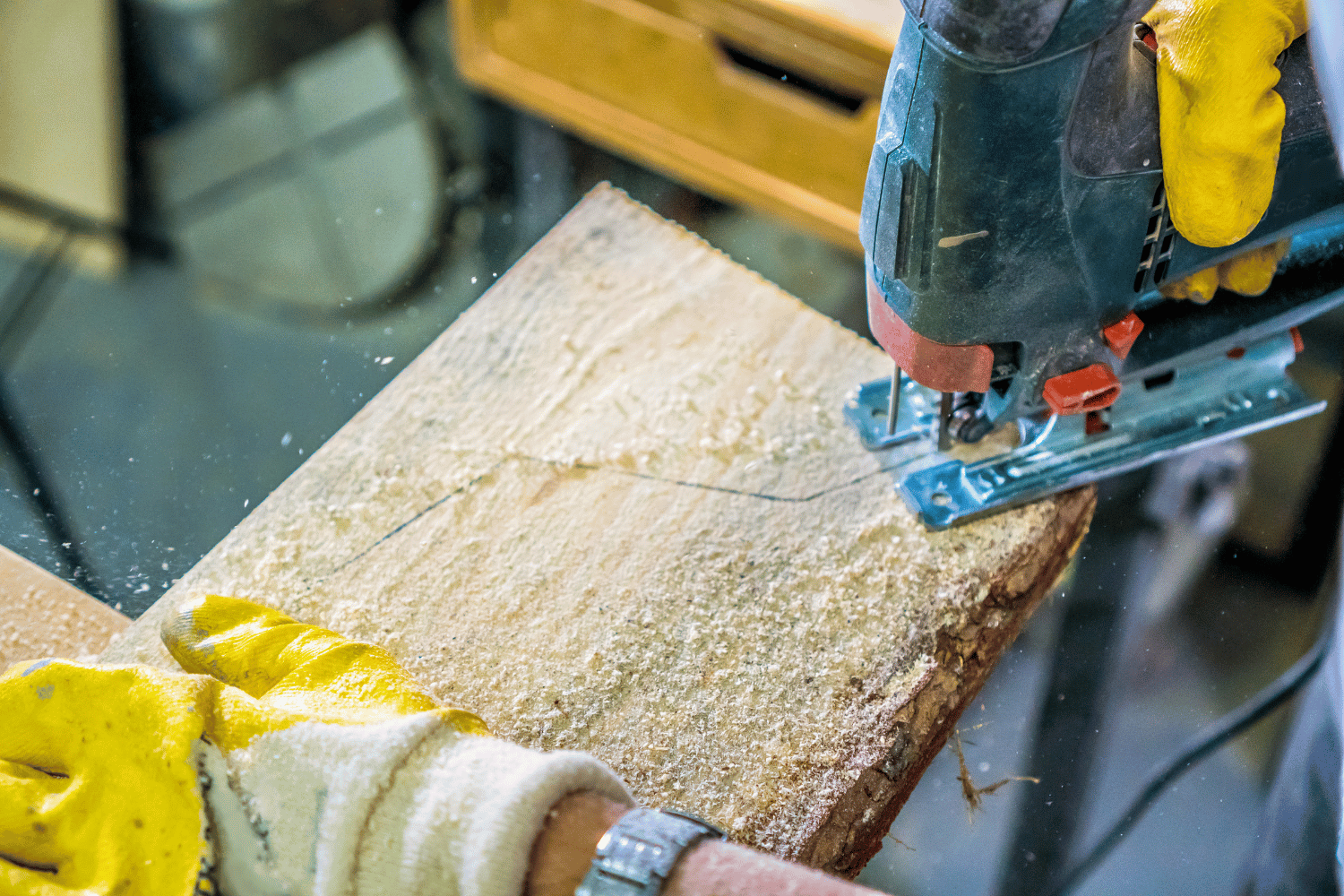

To ensure accurate and safe jigsaw use, follow these tips: apply painter’s tape to hold wood fibers in place and prevent tear out; use a straight edge guide for straight lines; drill a starter hole when cutting holes and openings; and always wear safety gear, such as safety glasses and a dust mask.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can maximize your jigsaw’s potential while minimizing the risk of accidents or damage to your workpiece.
Preventing Tear Out
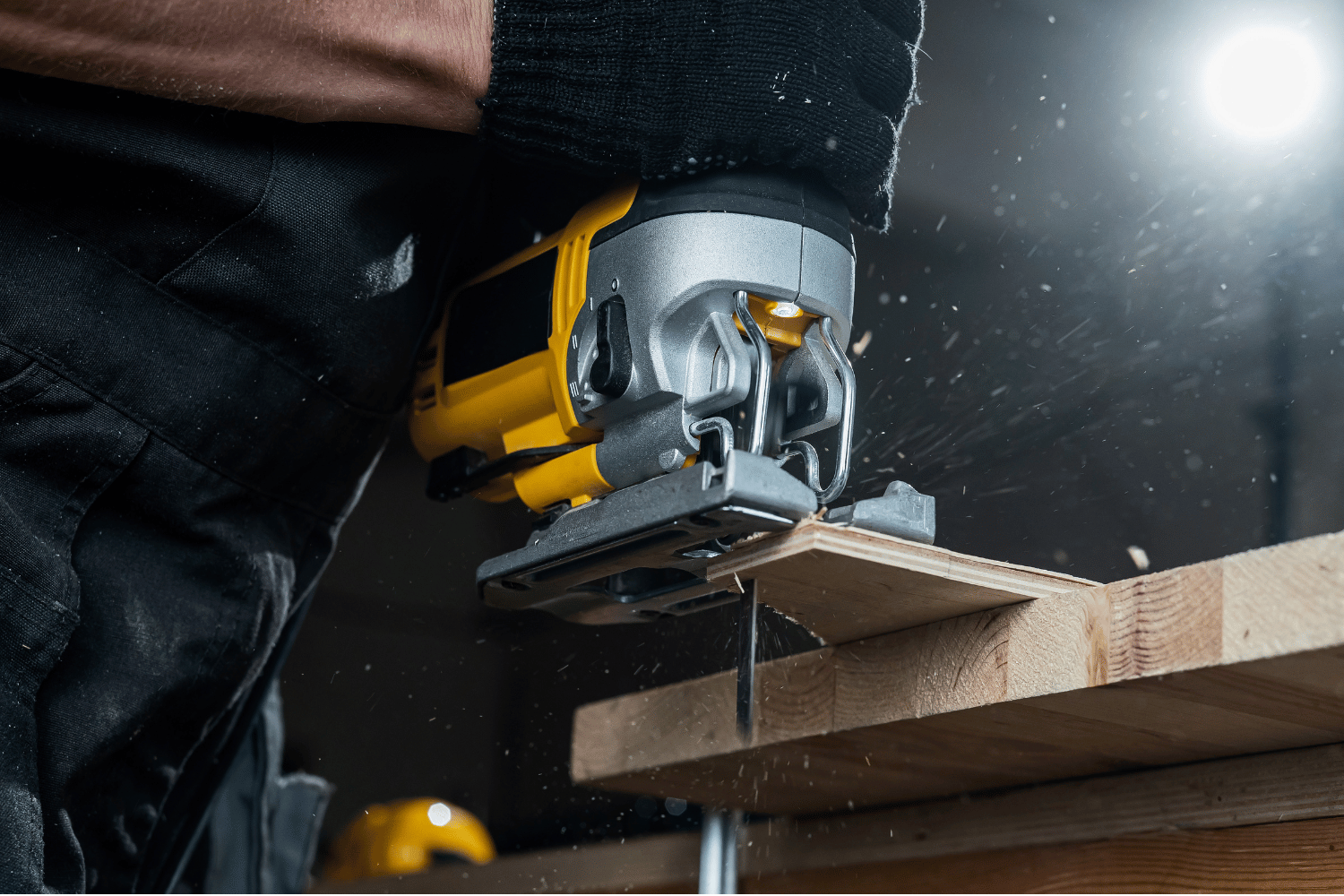

To prevent tear out when cutting with a jigsaw, you can use a zero-clearance shoe, which ensures a snug fit between the blade and the material being cut. Alternatively, you can apply blue painter’s tape to the cutting area to form a barrier between the blade and the material, helping to reduce the amount of material displaced from the blade and minimize tear out.
Creating a score or cut at the back of the workpiece can also help prevent tear out by providing an initial point for the blade.
Ensuring Straight Cuts
To ensure straight cuts with a jigsaw, use a straightedge or guide to follow the cutting line. This will help you cut straight lines more accurately, even if you are a beginner or still getting used to the tool.
Remember, achieving a straight line while using a jigsaw requires practice and patience, so take your time and let the blade do the work.
Safety Precautions
When using a jigsaw, it is important to prioritize safety. Always wear protective eyewear, gloves, and a dust mask. Secure the material with a clamp before cutting, and ensure the blade is sharp and properly installed.
Leaving space underneath the workpiece provides the necessary clearance for the blade to move and avoids the risk of it cutting into something unintended. By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure a successful project outcome.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, a jigsaw is a versatile and essential tool for any DIY enthusiast or professional craftsman. By understanding its components and capabilities, learning various cutting techniques, mastering advanced applications, and following safety precautions, you can unlock its full potential and tackle a wide range of projects with confidence. Whether you’re cutting curves, straight lines, or intricate shapes, a jigsaw is the perfect tool to help you achieve your creative vision and bring your ideas to life.