How to Use a Reciprocating Saw Like a Pro
Have you ever been in the middle of a DIY project, struggling to cut through a stubborn piece of wood or metal, and wish you had a tool that could make the job easier? Enter the reciprocating saw – a powerful and versatile tool that can cut through almost any material with ease. In this guide, we’ll show you how to use a reciprocating saw like a pro, so you can tackle any project with confidence.
Short Summary
- Reciprocating saws are versatile and powerful tools used in construction, demolition, and rescue operations.
- The right blade for a particular material is essential to getting professional results with a reciprocating saw.
- Safety precautions should be taken when using this tool, including wearing protective gear and following best practices such as wall scanning for hidden hazards.
Understanding Reciprocating Saws
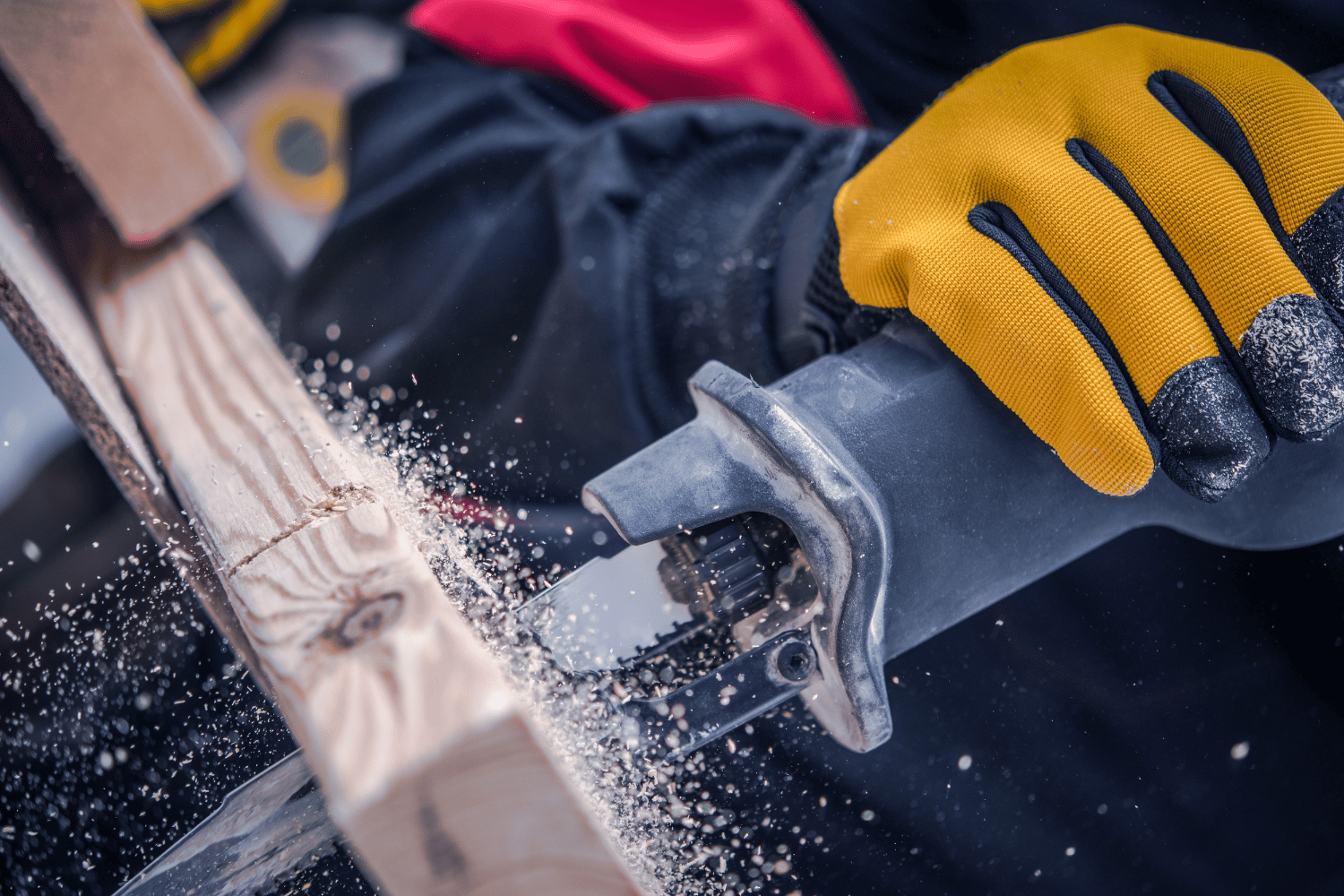

Reciprocating saws are handheld power tools designed for cutting through a wide variety of materials, such as wood, metal, and plastic. These saws, a type of power tool, feature a long, exposed reciprocating blade that moves back and forth at high speed, providing the cutting action. They are commonly used in construction, demolition, and rescue operations due to their ability to cut through walls, obstacles, or debris with ease. The versatility of reciprocating saws makes them a must-have tool for any DIY enthusiast or professional contractor.
There are several types of reciprocating saws available, including corded and cordless models, as well as different blade types designed for specific materials and tasks. Some reciprocating saws also feature orbital action, which means the blade moves in an elliptical motion for faster cutting, albeit with more vibration and a rougher finish. By choosing the right saw and blade for your needs, you can easily cut through tree branches, plumbing pipes, or even ceramic tile without breaking a sweat.
Choosing the Right Blade for Your Project
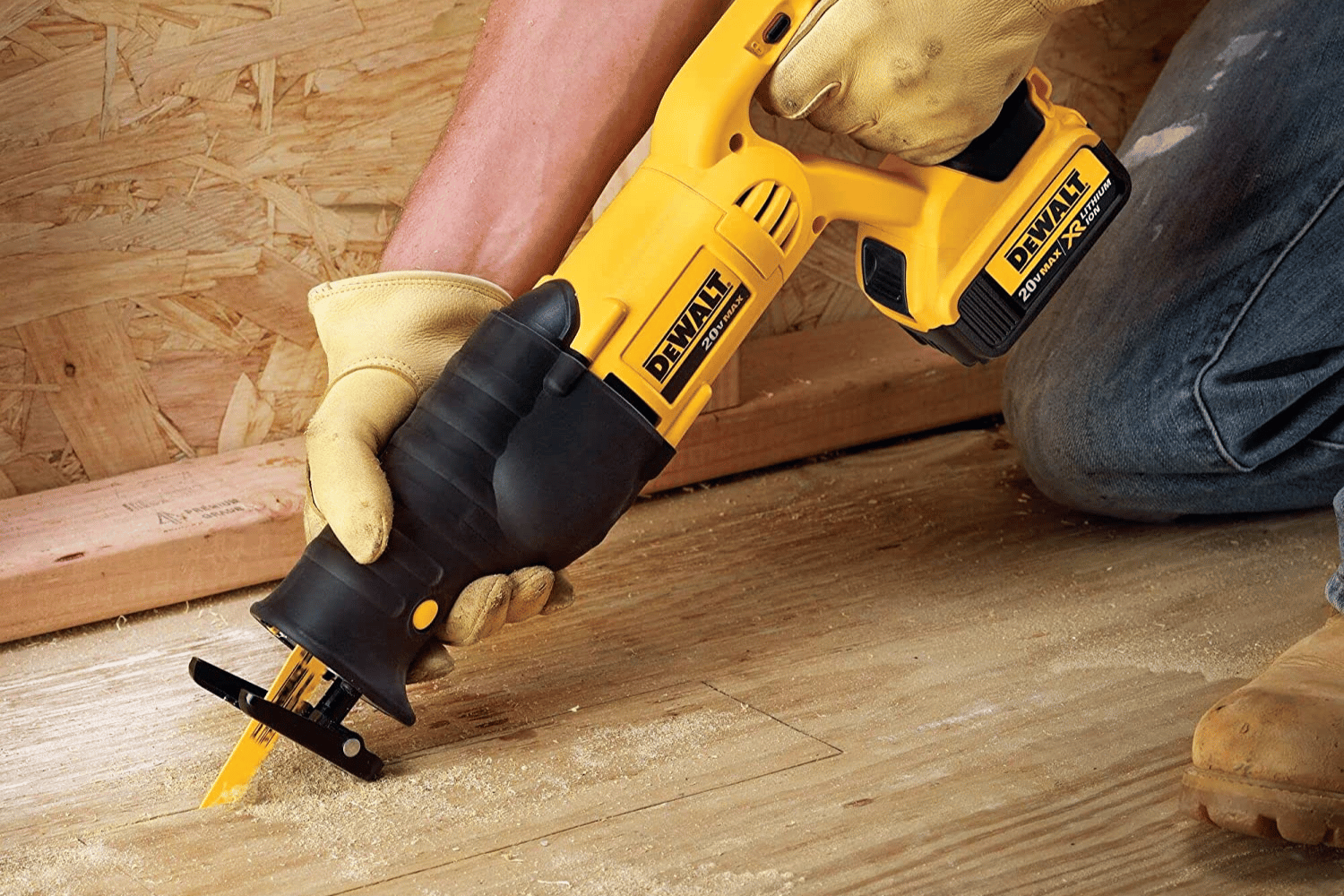

One crucial aspect of using a reciprocating saw like a pro is selecting the right blade for the material you’re cutting. Different saw blade options are available for different materials, such as wood, metal, and specialty reciprocating saw blade types.
In the following subsections, we’ll discuss each blade type in more detail to help you choose the right one for your project.
Wood Cutting Blades
Wood cutting blades are designed specifically for cutting through wood or plastic materials. They come in various types, including rip blades, crosscut blades, combination blades, and specialty blades, each with their unique purpose. For example, a rip blade is ideal for cutting along the grain of the wood, while a crosscut blade is perfect for making cuts across the grain.
When using a reciprocating saw for pruning trees or shrubs, a wood cutting blade is the best choice, as it can provide clean cuts without damaging the surrounding area. For tasks that involve cutting through wood with nails, such as demolition work, a wood and nail blade is recommended to prevent damage to the blade and ensure a smooth cutting process.
Metal Cutting Blades

Metal cutting blades, with their precise blade tip, are designed to cut through various metals, such as sheet metal, steel pipes, angle irons, tubing, and aluminum. The optimal blade for cutting metal depends on the thickness and type of metal being cut. For example, 18-24 TPI (teeth per inch) bi-metal blades are recommended for cutting thin metals, while 14-18 TPI bi-metal blades are suitable for thicker metals like steel pipes or angle irons.
Cutting metal with a reciprocating saw requires patience and the right technique. It’s essential to use the appropriate metal cutting blade, wear safety glasses, and apply a slow and consistent cutting motion without forcing the blade through the material. Lubricating the blade with cutting oil can also help reduce friction and heat buildup, prolonging the blade’s life and ensuring a smoother cut.
Specialty Blades
Specialty blades, including those with a slightly curved blade, are designed for specific tasks or materials that may not be covered by standard wood or metal cutting blades. These blades can be used for a variety of applications, such as ripping lumber, cutting veneered plywood and panels, cutting laminates and plastics, and making intricate cuts.
When selecting a specialty blade for your reciprocating saw, it’s essential to choose one that’s designed for the task and material at hand. Always check the blade’s packaging or markings to ensure it’s suitable for the specific material you’ll be cutting. Using the right specialty blade will ensure a smooth and efficient cutting process, helping you achieve the best results possible.
Installing and Changing Blades Safely
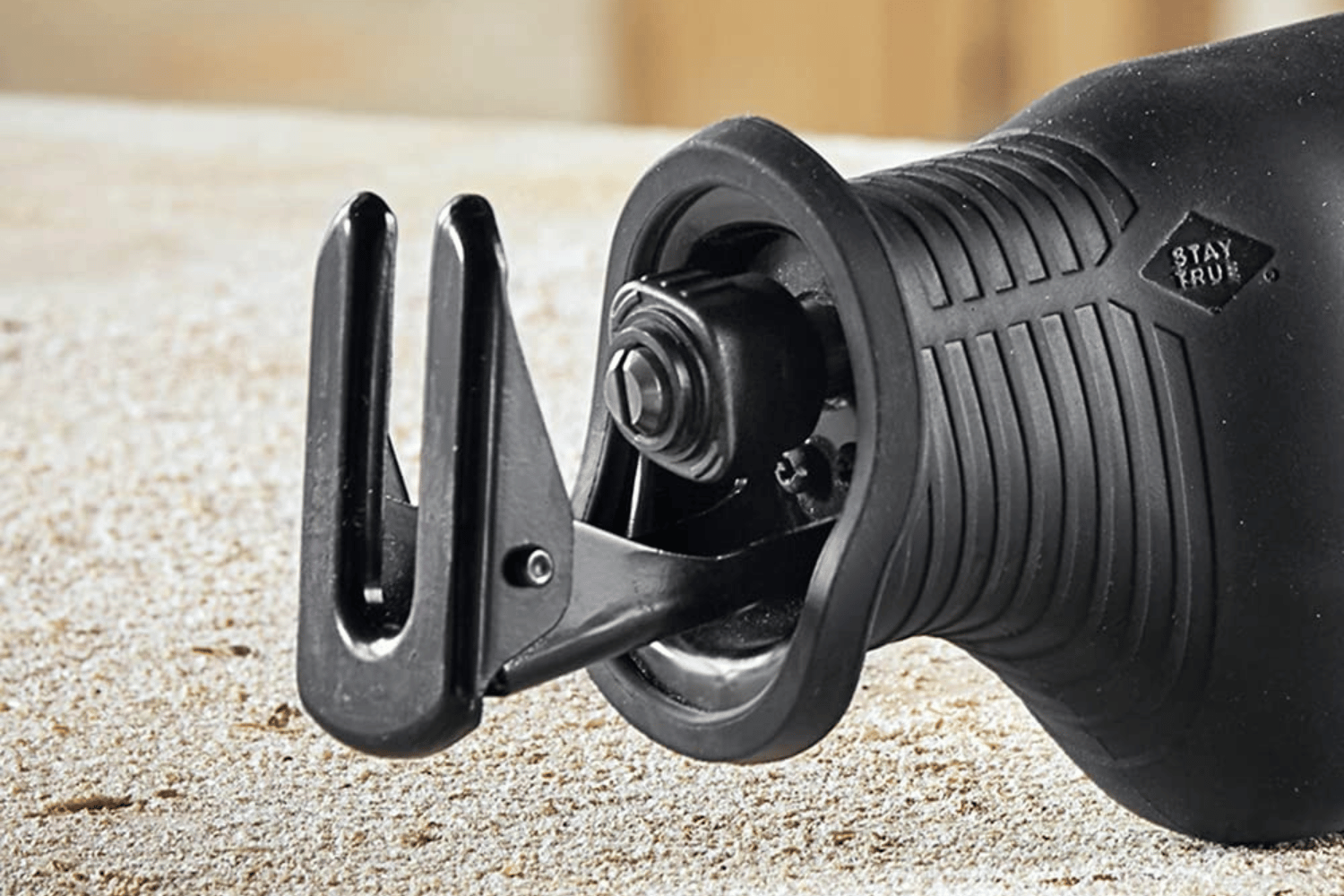
To install or change a blade on your reciprocating saw, first, unplug the saw or remove the battery pack to prevent accidental activation. Most reciprocating saws have a tool-free blade lock mechanism, making the process quick and easy. Simply open the blade clamp, insert the new blade with the teeth facing away from the saw’s handle, and close the clamp to secure the blade in place.
Once the blade is installed, reconnect the power source and make sure the blade intersection won’t come into contact with any objects during cutting. Always use caution when installing or changing blades, as mishandling could lead to injury or damage to the saw.
Proper Cutting Techniques for Various Materials

Different materials require different cutting techniques to ensure a smooth and efficient cutting process. In the following subsections, we’ll discuss proper cutting techniques for wood, metal, and plastic, so you can get the most out of your reciprocating saw and achieve professional results.
For wood, the best technique is to use a slow, steady motion with the saw blade. Make sure to keep the blade perpendicular to the wood surface to ensure a smooth surface.
Cutting Wood
When cutting wood with a reciprocating saw, it’s crucial to use the right blade and technique to achieve clean, precise cuts. For example, when making a plunge cut (an internal cut without an initial entry point), use a power drill to create a hole in the material, then insert the blade into the hole and start cutting.
When cutting wood with nails, use a wood and nail blade to prevent damage to the blade and ensure a smooth cutting process. To achieve the best results, maintain a firm grip on the saw, keep the blade perpendicular to the material, and use a variable speed trigger to control the cutting speed. This will help you achieve precise cuts and avoid damaging the material.
Cutting Metal
Cutting metal with a reciprocating saw requires a different approach than cutting wood. To ensure a smooth and efficient cutting process, use the appropriate metal cutting blade and follow safety precautions such as wearing safety glasses. When cutting metal, it’s important to apply a slow and consistent cutting motion without forcing the blade through the material. Lubricating the blade with cutting oil can also help reduce friction and heat buildup, prolonging the blade’s life and ensuring a smoother cut.
When cutting metal pipes or tubing, use a 14-18 TPI bi-metal blade for thicker metals and an 18-24 TPI bi-metal blade for thinner metals. By using the right blade and technique, you’ll be able to cut through metal with ease and precision.
Cutting Plastic
Cutting plastic with a reciprocating saw requires a different approach than cutting wood or metal. To ensure a smooth and efficient cutting process, use a wood-cutting blade with 10 teeth per inch, as this will provide clean cuts without damaging the material. When cutting plastic, it’s important to apply a slow and steady cutting motion, maintaining the blade perpendicular to the material and using light pressure to achieve a clean cut.
To prevent accidents and injuries while cutting plastic, always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect against flying debris. By following these safety precautions and using the right blade and technique, you’ll be able to cut through plastic materials with ease and precision.
Making Precise Cuts with a Reciprocating Saw
Achieving precise cuts with a reciprocating saw takes practice and patience. One way to improve the accuracy of your cuts is by using a jigsaw, which is designed for making intricate cuts with greater precision than a reciprocating saw. Alternatively, you can use a circular saw or a straight edge guide to help you make straight cuts. Simply attach the guide to the workpiece and use it to guide the saw along the desired cut line.
Another technique for making precise cuts is to tilt the saw slightly towards you, with the tip of the blade pointing up into the air. This allows you to see the cutting line more easily and helps to keep the blade straight. By using these techniques and practicing your cutting skills, you’ll be able to achieve precise cuts with a reciprocating saw every time.
Using Attachments for Additional Functions
In addition to cutting, a reciprocating saw can also be used for a variety of other tasks, thanks to a range of available attachments. These attachments can be used for sanding, polishing, scraping, removing adhesives, and even grout removal.
In the following subsections, we’ll discuss each attachment type and its uses to help you get the most out of your reciprocating saw.
Sanding and Polishing
While reciprocating saws are not typically used for sanding and polishing tasks, certain attachments can make these jobs possible. Sanding pads, scouring pads, and wire brush attachment can be used with a reciprocating saw to sand wood, polish metal surfaces, debur, and remove rust.
To use a reciprocating saw for sanding and polishing tasks, simply attach the appropriate sanding or polishing attachment to the saw and adjust the speed accordingly. Be sure to wear protective gear, such as safety glasses and gloves, to protect yourself from flying debris and dust.
Scraping and Removing Adhesives
A reciprocating saw can also be used for scraping and removing adhesives, such as glue, mastic, or caulking, with the help of a scraper blade attachment. These scraper blades are designed to slip beneath the adhesive material, allowing each thrust of the scraper to lift up more adhesive, making it more efficient than manual scraping.
To use a reciprocating saw for scraping and removing adhesives, attach the scraper blade to the saw and adjust the speed accordingly. Be sure to wear protective gear, such as safety glasses and gloves, to protect yourself from flying debris and dust.
Grout Removal
A reciprocating saw can be a handy tool for grout removal tasks, especially when using a grout rake attachment. This attachment is designed to extract existing grout between tiles when retiling a shower or other tiled surfaces. Carbide-grit blades are recommended for optimal grout removal.
To use a reciprocating saw for grout removal, attach the grout rake attachment or carbide-grit blade to the saw and adjust the speed accordingly. Be sure to wear protective gear, such as safety glasses and a dust mask, as well as ensure the area is well-ventilated.
Safety Tips and Best Practices
Safety should always be a priority when using a reciprocating saw. To protect yourself from potential injuries, always wear personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask, when operating the saw. Additionally, maintain a firm grip on the saw to prevent kickback and avoid cutting electrical wires or plumbing.
To further minimize the risk of accidents, use an AC detector or wall scanner to locate and avoid hidden hazards, such as electrical wires or plumbing, before cutting. By following these safety tips and best practices, you can confidently use a reciprocating saw for a wide range of projects while staying safe and protected.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Common issues with reciprocating saws include blade binding, kickback, and overheating. To troubleshoot these issues, first, check the blade to ensure it is sharp and properly installed. If the blade is not the issue, inspect the motor and replace it if necessary.
To avoid overheating, ensure the blade is adequately cooled and the battery is fully charged and properly installed. To prevent blade binding and kickback, maintain a firm grip on the saw, keep the blade perpendicular to the material, and use a variable speed trigger to control the cutting speed.
By addressing these common issues, you can prevent accidents and damage to your reciprocating saw, ensuring it works properly for years to come.
Corded vs. Cordless Reciprocating Saws
Both corded and cordless reciprocating saws have their advantages and disadvantages. A corded reciprocating saw typically offers greater power and is ideal for heavy-duty tasks, but its range is restricted by the length of the power cord. On the other hand, a cordless reciprocating saw offers increased portability and ease of use in locations with limited access to electrical outlets, although they may be less powerful than their corded counterparts.
When choosing between a corded and cordless reciprocating saw, consider factors such as the power source, weight, and any additional features, such as a built-in LED light or work light. Ultimately, the best reciprocating saw for your needs will depend on the specific tasks you plan to tackle and your personal preferences.
Maintenance and Care for Your Reciprocating Saw

Proper maintenance and care of your reciprocating saw will help extend its life and ensure it works properly. Regularly clean the saw to remove accumulated oil and dirt, using a clean cloth and avoiding solvents or harsh cleaning agents. Apply a few drops of non-flammable liquid lubricant to the moving parts of the saw to keep it running smoothly.
When storing your reciprocating saw, choose a dry environment free from moisture and extreme temperatures to prevent rust and damage to the saw’s components. By properly maintaining and caring for your reciprocating saw, you can enjoy years of reliable performance.
Final Thoughts
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve covered everything you need to know to use a reciprocating saw like a pro, from understanding the different types of saws and blades to proper cutting techniques for various materials and troubleshooting common issues. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any project with confidence, knowing you have the right tool and the right skills to get the job done.







